Name
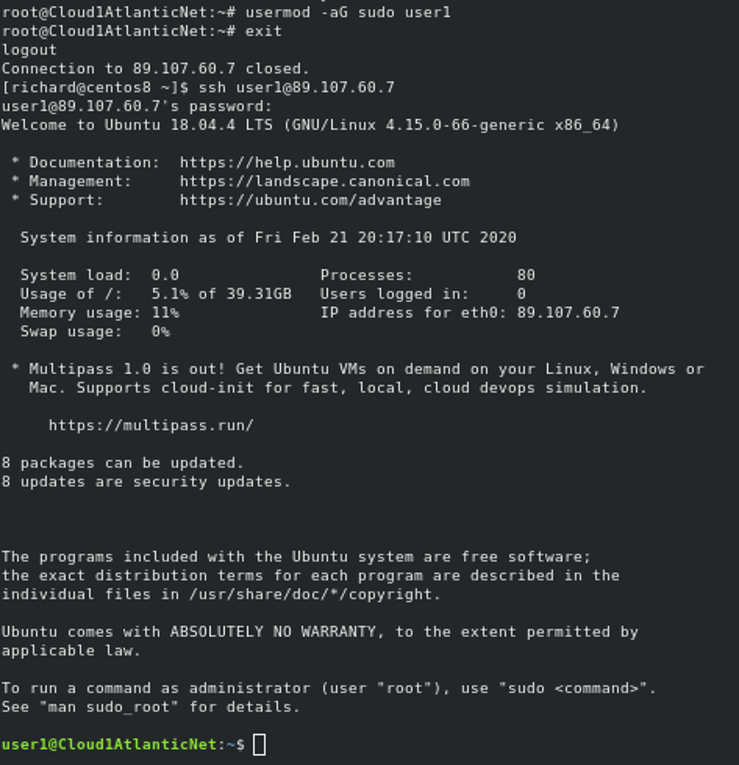
The adduser command equivalent for Mac is: dscl.create /User/USERNAMEHERE You may need admin privledges, therefore sudo will be needed like so.create /User/USERNAMEHERE Followed by a long chain of commands to set up that user properly. Linux provides usermod command by default for the most of the distributions. This command is used to user modification. After user creation the user related information, values and policies can be changed with usermod command. In this tutorial we will look various features of usermod command with examples.
usermod - modify a user account
Synopsis
usermod [options] LOGIN
Description
Usermod For Mac Os X
The usermod command modifies the system account files to reflect the changes that are specified on the command line.
Options
The options which apply to the usermod command are:
-a, --append
If the -m option is given, the contents of the current home directory will be moved to the new home directory, which is created if it does notalready exist.
A value of 0 disables the account as soon as the password has expired, and a value of -1 disables the feature.
If the user is currently a member of a group which is not listed, the user will be removed from the group. This behaviour can be changed via the -aoption, which appends the user to the current supplementary group list.
Note: if you wish to lock the account (not only access with a password), you should also set the EXPIRE_DATE to 1.
This option is only valid in combination with the -d (or --home) option.
Note: This option is not recommended because the password (or encrypted password) will be visible by users listing the processes.
You should make sure the password respects the system's password policy.
This value must be unique, unless the -o option is used. The value must be non-negative. Values between 0 and 999 are typically reserved for systemaccounts.
The user's mailbox, and any files which the user owns and which are located in the user's home directory will have the file user ID changed automatically.
The ownership of files outside of the user's home directory must be fixed manually.
 -L.
-L.Note: if you wish to unlock the account (not only access with a password), you should also set the EXPIRE_DATE (for example to 99999, or tothe EXPIRE value from /etc/default/useradd).
Caveats
You must make certain that the named user is not executing any processes when this command is being executed if the user's numerical user ID, the user'sname, or the user's home directory is being changed. usermod checks this on Linux, but only check if the user is logged in according to utmp on otherarchitectures.
You must change the owner of any crontab files or at jobs manually.
You must make any changes involving NIS on the NIS server.
Configuration
The following configuration variables in /etc/login.defs change the behavior of this tool:
MAIL_DIR (string)
If MAIL_CHECK_ENAB is set to yes, they are also used to define the MAIL environment variable.
MAX_MEMBERS_PER_GROUP (number)
Maximum members per group entry. When the maximum is reached, a new group entry (line) is started in /etc/group (with the same name, same password, and sameGID).The default value is 0, meaning that there are no limits in the number of members in a group.
This feature (split group) permits to limit the length of lines in the group file. This is useful to make sure that lines for NIS groups are not larger than1024 characters.
If you need to enforce such limit, you can use 25.
Note: split groups may not be supported by all tools (even in the Shadow toolsuite). You should not use this variable unless you really needit.
Files
/etc/group
- Usermod For Mac Commands
See Also
chfn(1), chsh(1), passwd(1), crypt(3), gpasswd(8), groupadd(8), groupdel(8), groupmod(8),login.defs(5), useradd(8), userdel(8).